health transformation . institute
knowledge platform & advisory consulting
Joaquim Cardoso MSc
Chief Researcher, Editor & Advisor
December 30, 2022
SOURCE:
Einstein Journal
19/Dec/2022
Fernanda Vieira Paladino , Tarso Augusto Duenhas Accorsi , Bárbara Yasmin Gueuvoghlanian-Silva , Marcia Aparecida de Almeida , João Carlos Barbosa , Miguel Almeida de Oliveira Filho , Carlos Henrique Sartorato Pedrotti , Karine De Amicis , Claudio Luiz Lottenberg , Eduardo Cordioli
Highlights
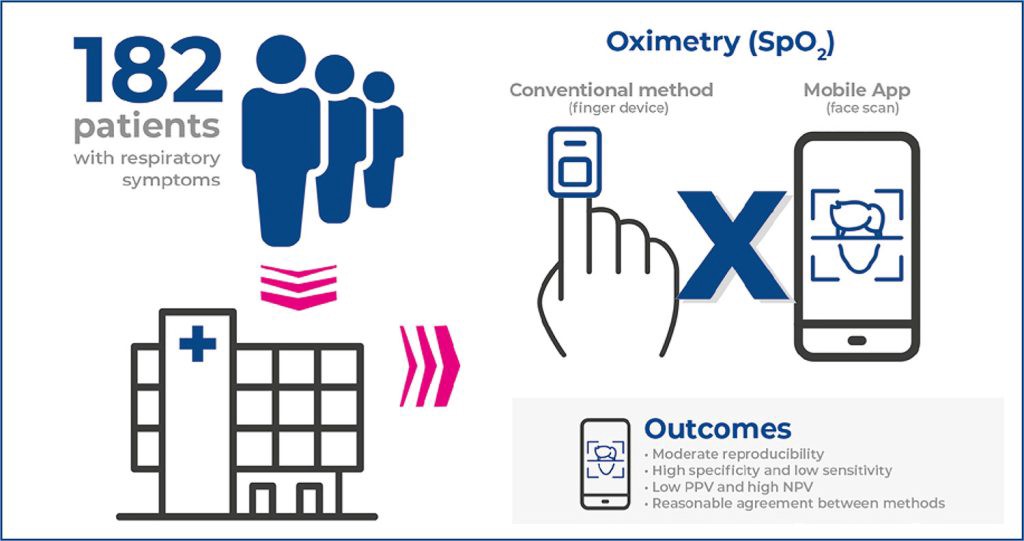
- The evaluated method showed moderate reproducibility when compared to the gold standard practice.
- This new method had a high specificity and a low sensitivity.
- The observed high range of SpO2 levels between the methods could lead to a wrong patient referral.
- The use of telemedicine to assess oxygen saturation in patient with dyspnea is a viable resource, although requiring improvement.
The use of telemedicine to assess oxygen saturation in patient with dyspnea is a viable resource, although requiring improvement.
ABSTRACT
Objective
- To calculate the positive likelihood ratio to determine whether telemedicine is able to optimize referral to the emergency department.
Methods
- Unicenter study with 182 consecutive patients admitted to Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein due to respiratory symptoms.
- All patients were submitted to oxygen saturation measurement using the standard method Welch Allyn finger device vital sign monitor and a 2-minute evaluation (Binah.ai mobile application).
- The reproducibility of oxygen saturation measurements made with both methods was investigated using interclass correlation coefficients and analysis of dispersion.
- Bland-Altman plots were constructed and kappa concordance coefficients used to examine data normality. Accuracy was also estimated.
Results
- Oxygen saturation measurement differences between methods were ≤2% in more than 85% of cases.
- The mean difference (bias) between methods was near zero (0.835; Bland-Altman analysis
- Oxygen saturation measurements made using the Binah.ai mobile application had an average ability to detect patients with altered oxygen saturation levels compared to the conventional method (ROC analysis).
- The positive likelihood ratio of the mobile application was 6.23.
Conclusion
- Mobile applications for oxygen saturation measurement are accessible user-friendly tools …
- … with moderate impact on clinical telemedicine evaluation of patients with respiratory symptoms, and …
- … may optimize referral to the emergency department.
Mobile applications for oxygen saturation measurement are accessible user-friendly tools …
… with moderate impact on clinical telemedicine evaluation of patients with respiratory symptoms, and …
… may optimize referral to the emergency department
Originally published at https://journal.einstein.br.
RELATED ARTICLES