the health strategist
institute for strategic health transformation
& digital technology
Joaquim Cardoso MSc.
Chief Research and Strategy Officer (CRSO),
Chief Editor and Senior Advisor
October 3, 2023
One page summary
What is the message?
The Time article discusses the critical state of the planet Earth, highlighting that humanity has reached a saturation point in terms of environmental limits.
It emphasizes the urgent need for immediate and exponential changes to address the challenges posed by climate change, biodiversity loss, and other planetary boundaries.

Key Takeaways
Planetary Boundaries:
Earth system science reveals that six out of nine biophysical systems and processes that regulate the state of the planet have exceeded their boundaries, putting humanity at risk of undermining livability in various aspects, including water, food, and health.
Climate Tipping Points:
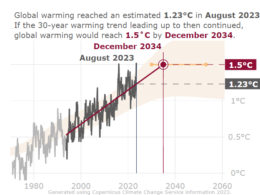
The article identifies four climate tipping point systems, including the Greenland Ice sheet, West Antarctic Ice sheet, tropical coral reef systems, and permafrost thawing, which are at risk of crossing their tipping points at 1.5°C of global warming, potentially leading to catastrophic consequences.
Justice and Climate:
The concept of climate justice is discussed, with the “just climate boundary” set at 1°C of warming. The article highlights that unacceptable harm will affect millions of people worldwide even before reaching the 1.5°C limit.
Urgent Actions Needed:
To address these challenges, the world must take immediate and exponential actions, including cutting global emissions in half by 2030, achieving a net-zero global economy by 2050, and halting the loss of species while building a nature-positive trajectory by 2030.
Systemic Approaches:
The article emphasizes the need for systemic and unified approaches, addressing all planetary boundaries simultaneously, rather than focusing solely on decarbonizing the global energy system.
Global Collaboration:
Collaboration and concerted efforts across all sectors, countries, and citizens are essential to solve the planetary crisis.
Earth Resilience:
Earth’s capacity to buffer climate impacts is decreasing due to factors like deforestation, land degradation, and marine system stress, making the need for rapid action even more critical.
Transformative Change:
Incremental and linear changes are no longer sufficient. The world must embrace exponential transformations across various sectors, integrating innovations, sustainable technologies, circularity, and equity.
Global Governance:
A reform in global governance is required to collectively manage all global commons that regulate the planet’s stability, including the climate system and Earth’s biophysical systems.
Positive Tipping Points:
Achieving positive social tipping points, where incentives, solutions, or levers of change fundamentally shift societies towards sustainability, is crucial.
Justice and Equity:
Addressing wealth distribution and poverty is essential for ensuring that the majority of citizens and societies can participate in the race to sustainability.
Sustainability as a Path:
Sustainability is not just an environmental issue but a path toward modernity 2.0. It offers competitive and cost-efficient solutions in many economic sectors.
DEEP DIVE

This summary was written based on the article “What the Latest Health Check Tells Us About the State of Our Planet”, published by Time and written by Johan Rockström, on September 22, 2023.
About the Author
Johan Rockström is a Professor of Earth System Science at the University of Potsdam and the Director Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research