Healthcare Transformers
Simone Edelmann, PhD, Editor at HealthcareTransformers.com
10 February 2020
What we aim to answer:
- What is personalized healthcare (PHC) and why is it the future of healthcare?
- What are the major market drivers and challenges of the PHC market?
- What are the technologies that can have the largest impact towards improving patient outcomes and delivery of care?
- What strategies can healthcare executives use to deliver personalized treatment and improve patient outcomes?
Quick Takes
- The advancement of medical knowledge, technology and data science is quickly transforming the healthcare landscape and paving the way towards personalized care
- Driving this revolutionary change is data and the ability to extract meaningful health insights
- Of course, as with any change, there are challenges to overcome.
From “one size fits all” to personalized healthcare
Until recently, there was a “one size fits all” approach to medicine: treat as many patients as possible with the same treatment. However, the observed outcomes of why some patients responded well to a certain therapy, while others did not, were poorly understood.
There became an urgent need to target specific medications to specific populations. With our improved understanding of human and disease biology and the advancement of modern diagnostics, this was made possible — as illustrated by the evolution of companion diagnostics.
Today we are at a pivotal moment in healthcare history. The digitization of high quality healthcare data, including diagnostic, treatment and outcome data from varying sources (ie. real world, clinical trials) has tremendous potential.
From this data, we will be able to answer key scientific questions and harness meaningful medical insights that will render a granular view of each individual patient.
This will lead to the personalization of healthcare
ensuring the right treatment
for the right patient
at the right time.
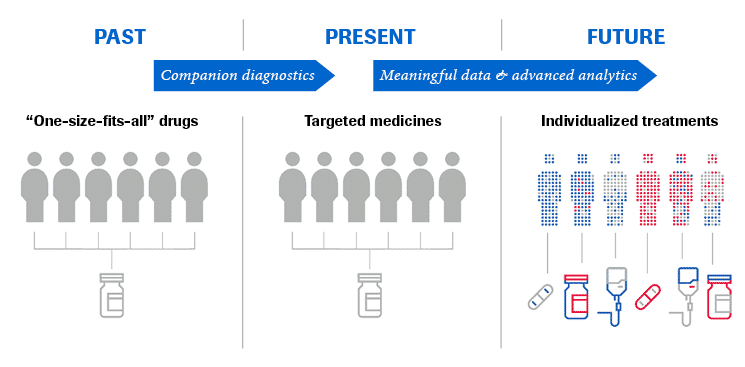
The many sides and benefits of personalized healthcare
Personalized healthcare (PHC), which includes the terms personalized medicine and precision medicine, aims to ensure that the screening, diagnosis, treatment and even prevention of diseases, will more quickly and effectively transform patients’ lives.
It is a multifaceted approach to patient care that encompasses: [1]
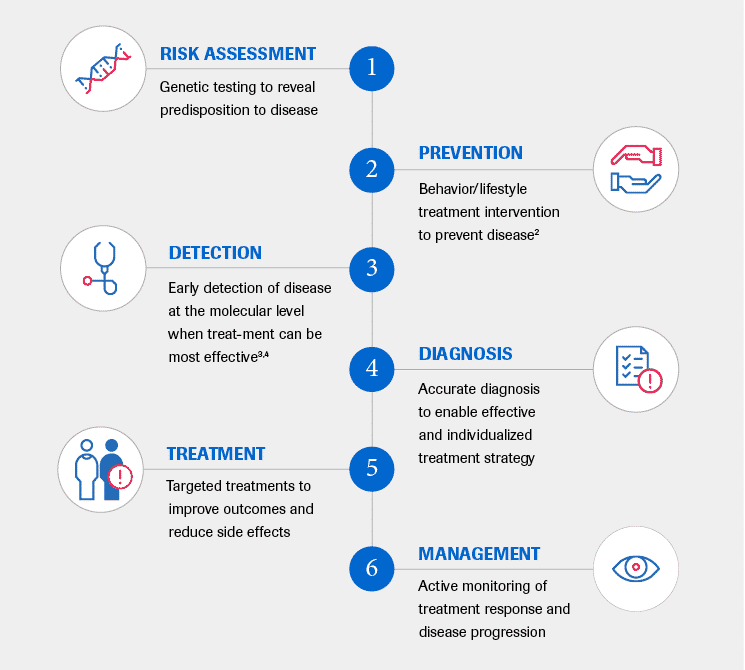
The potential benefits of PHC support both improved patient outcomes and a more efficient use of healthcare resources.
These include, but are not limited to:
1. Decreased trial-and-error medicine and potential adverse drug reactions
- Provide diagnostic tests to help identify patients most likely to respond (and not respond) to a specific treatment (eg. companion diagnostics)
- Aid in the development of safer treatments
2. Increased understanding of disease
- Understand contributing factors to disease manifestation and progression
- Identify and develop improved treatments and testing procedures
3. Increased provision of preventive healthcare
4. Increased speed and accuracy of diagnosis
5. Decreased time, burden and cost of drug development
- Predict pharmacogenetics in advance with simulations
- Allow for clinically meaningful trials on smaller patient subgroups qualified by specific biomarkers
Market opportunities and challenges
Drivers of industry growth
- Increasing prevalence and economic burden of chronic diseases
- Rapid advancements in relevant technologies
- Development of big data analytics solutions
- Growing healthcare expenditure
1.Increasing prevalence and economic burden of chronic diseases [5,6]
Chronic diseases, or noncommunicable diseases, are collectively responsible for almost 70% of all deaths worldwide. 7
According to the World Economic Forum, the cost of treating the five leading chronic diseases — cancer, diabetes, mental illness, heart disease, and respiratory disease — could reach US$ 47 trillion over the next 15 years. 8
A large part of chronic conditions may be prevented. [8,9]
PHC can help to identify at-risk patients for a number of chronic conditions, allowing for early diagnosis for a more successful treatment response, or even disease prevention through effective intervention.
2.Rapid advancements in relevant technologies [5,6]
The advancement of “omic” technologies such as genomics, transcriptomics and proteomics, have generated a deeper understanding of disease pathology and progression, and new methodologies for monitoring treatment response. 10–12
As relevant technologies, such as next-generation sequencing (NGS), become cheaper and more reliable and accessible, there will be a surge in their use to better classify and profile disease. In turn, this will drive a more personalized approach in managing and treating patients.
3.Development of big data analytics solutions [5]
The goal of PHC is to make collected health data of pragmatic value to clinicians. Routinely collected healthcare data is growing in complexity and volume. 13In 2020, it is estimated that the amount of medical data will reach 2,314 exabytes (1 exabyte = 1 billion gigabytes). 14 The principal types of big data in biomedical research stem from multiomics, imaging, device data, and electronic health records. 13
New methods dedicated to improving data collection, storage, cleaning, processing and interpretation continue to be developed at a rapid pace. Big data analytics and solutions software will be the key for healthcare providers to monetize their collected data and add value to their business, while improving health outcomes for patients.
4.Growing healthcare expenditure [5,6]
Global healthcare expenditure projected to reach just over US$ 10 trillion by 2022. [15]
Main cost drivers include: [15]
- Aging and growing populations
- Market expansion into developing countries
- Clinical and technology advancements
- Rising labor costs
Shifting the focus from “sickcare” to preventive healthcare that embraces a value-based over a fee-for-service-based delivery model will be crucial to the affordability, accessibility and sustainability of future healthcare systems. 15,16
PHC plays an essential role in this transition, which is already underway in advanced economies. 16
Challenges of industry growth
- Lack of data integrity
- Reimbursement coverage
- Regulatory uncertainty
1.Lack of data integrity
The success of PHC will rely on the integrity of stored health data — ie. the accuracy, completeness, and reliability of the data throughout its lifecycle. With the vast amount of data to call upon, there are indeed challenges which threaten data integrity stemming from: 17–19,28
- Data collection
- Data volume and complexity
- Data transformation
2.Reimbursement coverage [20,22]
As healthcare becomes more personalized, so does the complexity of pricing and reimbursement. Pricing should not only reflect the sum of the diagnostic tests or monotherapies used for a patient, but also the combined benefits delivered to patients, their families, payers and societies.
Payers increasingly want more evidence about the effectiveness of a new diagnostic or therapy, as well as the potential budget impact these treatments might have. Personalized healthcare solutions hold the potential to improve health outcomes, provided that their economical value can be demonstrated and data uncertainties addressed. [21]
3.Regulatory uncertainty [21]
Regulatory uncertainty is reported as one of the main barriers to realizing the potential of PHC. 22Existing regulations have been cited as being inapplicable to PHC interventions and the amount of data generated by new technologies, such as NGS, poses new challenges for regulation bodies. 23
The transformation of healthcare to a personalized approach will also require a transformation to the standards and protocols to assess personalized diagnostics and treatments. However, this change is already underway as shown by the number of “personalized medicine” approvals in recent years (42% of all 2018 new drug approvals as reported by the FDA). 24Furthermore, the International Consortium for Personalised Medicine, (ICPerMed) launched in 2016 has stated as an agenda item to establish Europe as a global leader in personalized medicine research. 25,26
How can your organization deliver more personalized care?
In summary, the advancement of medical knowledge, technology and data science is quickly transforming the healthcare landscape and paving the way to patient-centric personalized care.
Of course, as with any change, there are challenges to overcome.
We’ve put together 5 key strategies to help you on your journey towards delivering more personalized healthcare solutions.
References
See the full version of the article.
About the author
Simone Edelmann, PhD is an editor and contributor at HealthcareTransformers.com.
After completing her PhD from the Institute of Biotechnology at the University of Lausanne, Switzerland, she found her passion in medical and scientific communications.
She is dedicated to delivering high-quality content on the topic of the future of healthcare to our readers.
Originally published at https://healthcaretransformers.com on February 10, 2020.