Towards a G7 Common Understanding on Generative AI
the health strategist . institute
institute for
continuous health transformation
and digital health [data driven & AI powered]
Joaquim Cardoso MSc.
Chief Research Officer (CRO), Chief Editor,
Chief Strategy Officer (CSO), and
Independent Senior Advisor
oecd
September 2023
Overview
G7 leaders identified topics for discussion in the Hiroshima process and called for an early stock taking of opportunities and challenges related to generative AI. This report presents the results of a questionnaire developed to support the stocktaking to help guide G7 discussions on common policy priorities with regard to generative AI. It also provides a brief overview of the development of generative AI over time and across countries. The report and questionnaire results should be understood as representing a snapshot in time: they are indicative of trends identified in summer 2023 in a rapidly evolving area of technology. The report helped inform and structure discussions of the G7 Hiroshima AI Process.
This document was prepared by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) Directorate for Science Technology and Innovation (STI) for the 2023 Japanese G7 Presidency and the G7 Digital and Tech Working Group, to inform discussions during the G7 Hiroshima Artificial Intelligence Process and the related interim virtual Ministers’ Meeting on generative artificial intelligence on 7 September 2023. The opinions expressed and arguments employed herein do not necessarily reflect the official views of the member countries of the OECD or the G7.
This work is published under the responsibility of the Secretary-General of the OECD.
This document, as well as any data and map included herein, are without prejudice to the status of or sovereignty over any territory, to the delimitation of international frontiers and boundaries and to the name of any territory, city or area.
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
Generative AI has rapidly entered public discourse.
- Growth in generative AI research, including its open-source code development, preceded the surge in investments.
- Rapid advances in generative AI are driven by its expected potential to drive productivity gains and to promote innovation and entrepreneurship, as well as to unlock solutions to global challenges.
Yet, generative AI’s potential benefits come with risks.
- As these risks evolve rapidly, their management and mitigation is at the top of the agenda for G7 governments.
- G7 jurisdictions are evaluating their respective responses to generative AI, as well as the policy gaps.
G7 members are aligned on the need to provide effective tools for safety, quality control, and capacity and trust building for generative AI.

Generative AI has rapidly entered public discourse.
Generative AI has entered into public consciousness and is increasingly present in peoples’ everyday conversations worldwide. The number of news articles and tweets related to ‘generative AI’ grew eight-fold over just six months.
Growth in generative AI research, including its open-source code development, preceded the surge in investments.
The widespread awareness and rapid uptake of generative AI have been enabled by steady, incremental progress in both research and code development.
Fundamental innovations such as the ‘Transformers’ architectures, contributions of the open-source community, alongside improvement in computing power have paved the way for the proliferation of large language models as well as other type of generative AI models.
Scientific publications and open-source code development on generative AI have grown remarkably since 2017, and this trend accelerated in 2023.
Venture capital investments in generative AI have skyrocketed and were estimated at USD 12 billion globally in the first half of 2023 alone.
Scientific publications and software, including open-source code, related to generative AI have seen a parallel remarkable surge since 2017, with this trend further accelerating in 2023.
Rapid advances in generative AI are driven by its expected potential to drive productivity gains and to promote innovation and entrepreneurship, as well as to unlock solutions to global challenges.
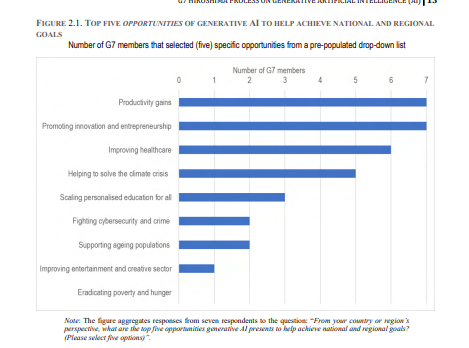
In a questionnaire administered in Q3 2023, G7 members unanimously saw productivity gains, promoting innovation and entrepreneurship and unlocking solutions to global challenges, as some of the greatest opportunities of AI technologies worldwide, including for emerging and developing economies.
G7 members also emphasised generative AI’s potential role to help address pressing societal challenges, such as
- improving healthcare and
- helping to solve the climate crisis, and
- to support progress towards achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Yet, generative AI’s potential benefits come with risks.
The capacity of generative AI to exacerbate the challenges of disinformation and manipulation of opinions is considered by G7 members as one of the major threats stemming from generative AI, alongside risks of intellectual property rights infringement and privacy breaches.
Early efforts to track AI incidents found one thousand distinct incidents and hazards related to generative AI, based on roughly 5 600 news articles dated from January to July 2023.
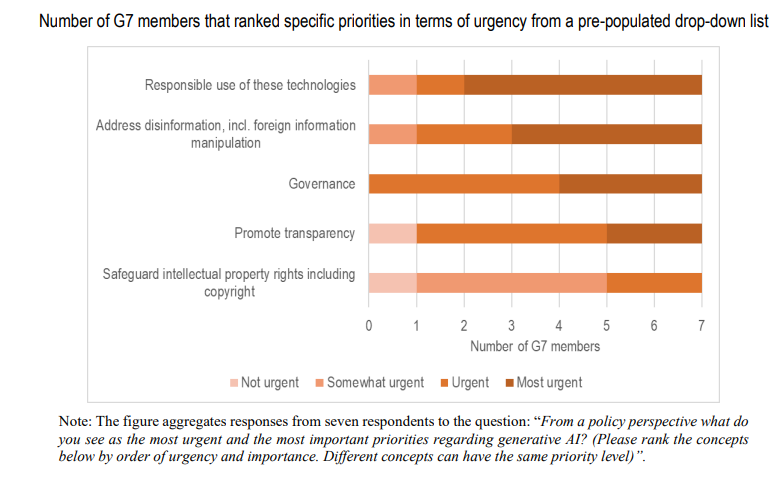
As these risks evolve rapidly, their management and mitigation is at the top of the agenda for G7 governments.
Responsible use of generative AI, addressing disinformation, safeguarding intellectual property rights, and governing generative AI are among the top priorities for G7 policymakers and require international cooperation with like-minded partners.
Other urgent and important issues emphasised by G7 members include privacy and data governance, transparency, fairness and bias, human and fundamental rights, security and robustness of AI systems, and impacts on the functioning of democracy.
G7 jurisdictions are evaluating their respective responses to generative AI, as well as the policy gaps.
Countries are leveraging existing and forthcoming legal and policy frameworks and developing guidelines or regulation to address risks related to generative AI.
National initiatives are also being strengthened to seize its opportunities.
New issues raised by generative AI appear to affect specific sectors in particular, such as education, media, and the workplace.
G7 members are aligned on the need to provide effective tools for safety, quality control, and capacity and trust building for generative AI.
Safety, quality control, capacity and trust building for generative AI were seen as among the most urgent and important international action the G7 could undertake.
Engaging in dialogue was also considered to be most urgent, and developing voluntary codes of conduct was identified as among the most important actions.
Originally published at
Infographic