the health strategist
knowledge platform
Joaquim Cardoso MSc.
Chief Research and Strategy Officer (CRSO)
Chief Editor and Senior Advisor
August 11, 2023
What is the message?
Generative AI has the potential to create $2.6 trillion to $4.4 trillion in value across industries through enhancing functions like marketing, software development, risk management, and drug discovery, while necessitating considerations for quality control, security, user expectations, and privacy.
Key takeaways:
- Generative AI has the potential to drive substantial value across industries, as revealed by our analysis of 63 different use cases.
- Depending on various factors such as function mix, importance, and industry scale, generative AI’s impact ranges from $2.6 trillion to $4.4 trillion in value creation.
- In the retail industry, including auto dealerships, generative AI could contribute around $310 billion in added value.
- By enhancing functions like marketing and customer interactions, generative AI can optimize performance and personalize offerings, amplifying existing AI-driven solutions.
- High-tech sectors stand to benefit significantly from generative AI, primarily by accelerating software development processes, which constitutes the majority of potential value creation.
- In the banking sector, generative AI offers the potential to enhance efficiency by assuming lower-value tasks in risk management, such as reporting, regulatory monitoring, and data collection.
- Additionally, it can improve customer satisfaction, decision-making, employee experiences, and fraud/risk monitoring.
- The pharmaceutical and medical-product industries have the potential to unlock significant value, ranging from $60 billion to $110 billion annually.
- Generative AI expedites drug discovery processes and offers automation, efficiency, and precision across various stages, from preliminary screening to indication finding.
- Incorporating generative AI presents opportunities and challenges. Retail and consumer packaged goods companies should consider quality control, security against adversarial attacks, and the integration of generative AI with existing AI solutions.
- Banks need to address regulation, user expectations, levels of automation, and data privacy.
- In the pharmaceutical sector, a “human in the loop” approach, explainability, and privacy concerns must be addressed.
- Generative AI stands as a transformative force across industries, empowering organizations to unlock unprecedented value, streamline operations, and enhance customer experiences.
Infographics:



DEEP DIVE

Industry Impacts [Generative AI – Part 3]
This is an excerpt of the report “The state of AI in 2023: Generative AI’s breakout year”, published by MGI (McKinsey Global Institute), authored by Michael Chui, Lareina Yee; Bryce Hall, Alex Singla and Alexander Sukharevsky, an issued on August, 2023.
MGI
Michael Chui, Eric Hazan, Roger Roberts, Alex Singla, Kate Smaje, Alex Sukharevsky, Lareina Yee, and Rodney Zemmel
June 14, 2023
Across the 63 use cases we analyzed, generative AI has the potential to generate $2.6 trillion to $4.4 trillion in value across industries. Its precise impact will depend on a variety of factors, such as the mix and importance of different functions, as well as the scale of an industry’s revenue (Exhibit 4).

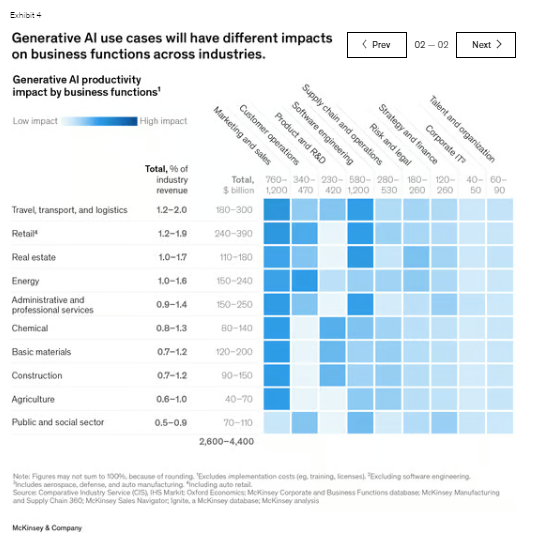
For example, our analysis estimates generative AI could contribute roughly $310 billion in additional value for the retail industry (including auto dealerships) by boosting performance in functions such as marketing and customer interactions. By comparison, the bulk of potential value in high tech comes from generative AI’s ability to increase the speed and efficiency of software development (Exhibit 5).

In the banking industry, generative AI has the potential to improve on efficiencies already delivered by artificial intelligence by taking on lower-value tasks in risk management, such as required reporting, monitoring regulatory developments, and collecting data. In the life sciences industry, generative AI is poised to make significant contributions to drug discovery and development.
We share our detailed analysis of these industries below.
Generative AI supports key value drivers in retail and consumer packaged goods
The technology could generate value for the retail and consumer packaged goods (CPG) industry by increasing productivity by 1.2 to 2.0 percent of annual revenues, or an additional $400 billion to $660 billion.1 To streamline processes, generative AI could automate key functions such as customer service, marketing and sales, and inventory and supply chain management. Technology has played an essential role in the retail and CPG industries for decades. Traditional AI and advanced analytics solutions have helped companies manage vast pools of data across large numbers of SKUs, expansive supply chain and warehousing networks, and complex product categories such as consumables. In addition, the industries are heavily customer facing, which offers opportunities for generative AI to complement previously existing artificial intelligence. For example, generative AI’s ability to personalize offerings could optimize marketing and sales activities already handled by existing AI solutions. Similarly, generative AI tools excel at data management and could support existing AI-driven pricing tools. Applying generative AI to such activities could be a step toward integrating applications across a full enterprise.
Generative AI at work in retail and CPG
Reinvention of the customer interaction pattern
Consumers increasingly seek customization in everything from clothing and cosmetics to curated shopping experiences, personalized outreach, and food—and generative AI can improve that experience. Generative AI can aggregate market data to test concepts, ideas, and models. Stitch Fix, which uses algorithms to suggest style choices to its customers, has experimented with DALL·E to visualize products based on customer preferences regarding color, fabric, and style. Using text-to-image generation, the company’s stylists can visualize an article of clothing based on a consumer’s preferences and then identify a similar article among Stitch Fix’s inventory.
Retailers can create applications that give shoppers a next-generation experience, creating a significant competitive advantage in an era when customers expect to have a single natural-language interface help them select products. For example, generative AI can improve the process of choosing and ordering ingredients for a meal or preparing food—imagine a chatbot that could pull up the most popular tips from the comments attached to a recipe. There is also a big opportunity to enhance customer value management by delivering personalized marketing campaigns through a chatbot. Such applications can have human-like conversations about products in ways that can increase customer satisfaction, traffic, and brand loyalty. Generative AI offers retailers and CPG companies many opportunities to cross-sell and upsell, collect insights to improve product offerings, and increase their customer base, revenue opportunities, and overall marketing ROI.
Accelerating the creation of value in key areas
Generative AI tools can facilitate copy writing for marketing and sales, help brainstorm creative marketing ideas, expedite consumer research, and accelerate content analysis and creation. The potential improvement in writing and visuals can increase awareness and improve sales conversion rates.
Rapid resolution and enhanced insights in customer care
The growth of e-commerce also elevates the importance of effective consumer interactions. Retailers can combine existing AI tools with generative AI to enhance the capabilities of chatbots, enabling them to better mimic the interaction style of human agents—for example, by responding directly to a customer’s query, tracking or canceling an order, offering discounts, and upselling. Automating repetitive tasks allows human agents to devote more time to handling complicated customer problems and obtaining contextual information.
Disruptive and creative innovation
Generative AI tools can enhance the process of developing new versions of products by digitally creating new designs rapidly. A designer can generate packaging designs from scratch or generate variations on an existing design. This technology is developing rapidly and has the potential to add text-to-video generation.
Factors for retail and CPG organizations to consider
As retail and CPG executives explore how to integrate generative AI in their operations, they should keep in mind several factors that could affect their ability to capture value from the technology:
- External inference. Generative AI has increased the need to understand whether generated content is based on fact or inference, requiring a new level of quality control.
- Adversarial attacks. Foundation models are a prime target for attack by hackers and other bad actors, increasing the variety of potential security vulnerabilities and privacy risks.
To address these concerns, retail and CPG companies will need to strategically keep humans in the loop and ensure security and privacy are top considerations for any implementation. Companies will need to institute new quality checks for processes previously handled by humans, such as emails written by customer reps, and perform more-detailed quality checks on AI-assisted processes such as product design.
Why banks could realize significant value
Generative AI could have a significant impact on the banking industry, generating value from increased productivity of 2.8 to 4.7 percent of the industry’s annual revenues, or an additional $200 billion to $340 billion. On top of that impact, the use of generative AI tools could also enhance customer satisfaction, improve decision making and employee experience, and decrease risks through better monitoring of fraud and risk.
Banking, a knowledge and technology-enabled industry, has already benefited significantly from previously existing applications of artificial intelligence in areas such as marketing and customer operations.1 Generative AI applications could deliver additional benefits, especially because text modalities are prevalent in areas such as regulations and programming language, and the industry is customer facing, with many B2C and small-business customers.2
Several characteristics position the industry for the integration of generative AI applications:
- Sustained digitization efforts along with legacy IT systems. Banks have been investing in technology for decades, accumulating a significant amount of technical debt along with a siloed and complex IT architecture.3
- Large customer-facing workforces. Banking relies on a large number of service representatives such as call-center agents and wealth management financial advisers.
- A stringent regulatory environment. As a heavily regulated industry, banking has a substantial number of risk, compliance, and legal needs.
- White-collar industry. Generative AI’s impact could span the organization, assisting all employees in writing emails, creating business presentations, and other tasks.
Generative AI at work in banking
Banks have started to grasp the potential of generative AI in their front lines and in their software activities. Early adopters are harnessing solutions such as ChatGPT as well as industry-specific solutions, primarily for software and knowledge applications. Three uses demonstrate its value potential to the industry.
A virtual expert to augment employee performance
A generative AI bot trained on proprietary knowledge such as policies, research, and customer interaction could provide always-on, deep technical support. Today, frontline spending is dedicated mostly to validating offers and interacting with clients, but giving frontline workers access to data as well could improve the customer experience. The technology could also monitor industries and clients and send alerts on semantic queries from public sources. For example, Morgan Stanley is building an AI assistant using GPT-4, with the aim of helping tens of thousands of wealth managers quickly find and synthesize answers from a massive internal knowledge base.4 The model combines search and content creation so wealth managers can find and tailor information for any client at any moment.
One European bank has leveraged generative AI to develop an environmental, social, and governance (ESG) virtual expert by synthesizing and extracting from long documents with unstructured information. The model answers complex questions based on a prompt, identifying the source of each answer and extracting information from pictures and tables.
Generative AI could reduce the significant costs associated with back-office operations. Such customer-facing chatbots could assess user requests and select the best service expert to address them based on characteristics such as topic, level of difficulty, and type of customer. Through generative AI assistants, service professionals could rapidly access all relevant information such as product guides and policies to instantaneously address customer requests.
Code acceleration to reduce tech debt and deliver software faster
Generative AI tools are useful for software development in four broad categories. First, they can draft code based on context via input code or natural language, helping developers code more quickly and with reduced friction while enabling automatic translations and no- and low-code tools. Second, such tools can automatically generate, prioritize, run, and review different code tests, accelerating testing and increasing coverage and effectiveness. Third, generative AI’s natural-language translation capabilities can optimize the integration and migration of legacy frameworks. Last, the tools can review code to identify defects and inefficiencies in computing. The result is more robust, effective code.
Production of tailored content at scale
Generative AI tools can draw on existing documents and data sets to substantially streamline content generation. These tools can create personalized marketing and sales content tailored to specific client profiles and histories as well as a multitude of alternatives for A/B testing. In addition, generative AI could automatically produce model documentation, identify missing documentation, and scan relevant regulatory updates to create alerts for relevant shifts.
Factors for banks to consider
When exploring how to integrate generative AI into operations, banks can be mindful of a number of factors:
The level of regulation for different processes. These vary from unregulated processes such as customer service to heavily regulated processes such as credit risk scoring.
Type of end user. End users vary widely in their expectations and familiarity with generative AI—for example, employees compared with high-net-worth clients.
Intended level of work automation. AI agents integrated through APIs could act nearly autonomously or as copilots, giving real-time suggestions to agents during customer interactions.
Data constraints. While public data such as annual reports could be made widely available, there would need to be limits on identifiable details for customers and other internal data.
Pharmaceuticals and medical products could see benefits across the entire value chain
Our analysis finds that generative AI could have a significant impact on the pharmaceutical and medical-product industries—from 2.6 to 4.5 percent of annual revenues across the pharmaceutical and medical-product industries, or $60 billion to $110 billion annually. This big potential reflects the resource-intensive process of discovering new drug compounds. Pharma companies typically spend approximately 20 percent of revenues on R&D,1 and the development of a new drug takes an average of ten to 15 years. With this level of spending and timeline, improving the speed and quality of R&D can generate substantial value. For example, lead identification—a step in the drug discovery process in which researchers identify a molecule that would best address the target for a potential new drug—can take several months even with “traditional” deep learning techniques. Foundation models and generative AI can enable organizations to complete this step in a matter of weeks.
Generative AI at work in pharmaceuticals and medical products
Drug discovery involves narrowing the universe of possible compounds to those that could effectively treat specific conditions. Generative AI’s ability to process massive amounts of data and model options can accelerate output across several use cases:
Improve automation of preliminary screening
In the lead identification stage of drug development, scientists can use foundation models to automate the preliminary screening of chemicals in the search for those that will produce specific effects on drug targets. To start, thousands of cell cultures are tested and paired with images of the corresponding experiment. Using an off-the-shelf foundation model, researchers can cluster similar images more precisely than they can with traditional models, enabling them to select the most promising chemicals for further analysis during lead optimization.
Enhance indication finding
An important phase of drug discovery involves the identification and prioritization of new indications—that is, diseases, symptoms, or circumstances that justify the use of a specific medication or other treatment, such as a test, procedure, or surgery. Possible indications for a given drug are based on a patient group’s clinical history and medical records, and they are then prioritized based on their similarities to established and evidence-backed indications.
Researchers start by mapping the patient cohort’s clinical events and medical histories—including potential diagnoses, prescribed medications, and performed procedures—from real-world data. Using foundation models, researchers can quantify clinical events, establish relationships, and measure the similarity between the patient cohort and evidence-backed indications. The result is a short list of indications that have a better probability of success in clinical trials because they can be more accurately matched to appropriate patient groups.
Pharma companies that have used this approach have reported high success rates in clinical trials for the top five indications recommended by a foundation model for a tested drug. This success has allowed these drugs to progress smoothly into Phase 3 trials, significantly accelerating the drug development process.
Factors for pharmaceuticals and medical products organizations to consider
Before integrating generative AI into operations, pharma executives should be aware of some factors that could limit their ability to capture its benefits:
- The need for a human in the loop. Companies may need to implement new quality checks on processes that shift from humans to generative AI, such as representative-generated emails, or more detailed quality checks on AI-assisted processes, such as drug discovery. The increasing need to verify whether generated content is based on fact or inference elevates the need for a new level of quality control.
- Explainability. A lack of transparency into the origins of generated content and traceability of root data could make it difficult to update models and scan them for potential risks; for instance, a generative AI solution for synthesizing scientific literature may not be able to point to the specific articles or quotes that led it to infer that a new treatment is very popular among physicians. The technology can also “hallucinate,” or generate responses that are obviously incorrect or inappropriate for the context. Systems need to be designed to point to specific articles or data sources, and then do human-in-the-loop checking.
- Privacy considerations. Generative AI’s use of clinical images and medical records could increase the risk that protected health information will leak, potentially violating regulations that require pharma companies to protect patient privacy.
Originally published at https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/mckinsey-digital