Low amount of healthy foods, including whole grains and fruits, more significant than high levels of unhealthy foods Dietary risks, such as high sodium intake, are an ‘equal opportunity killer’
IHME
April 3, 2019
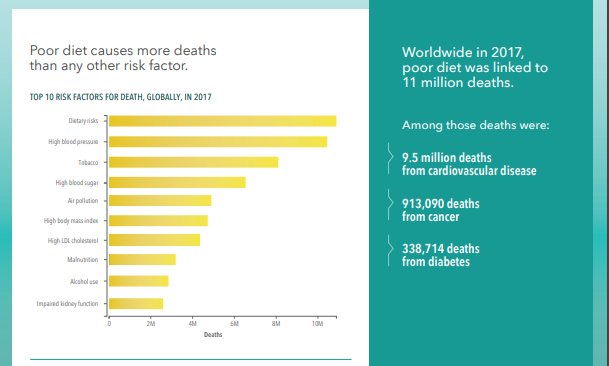
SEATTLE — Poor diet is responsible for more deaths globally than tobacco, high blood pressure, or any other health risk, according to a new scientific study.
Consuming low amounts of healthy foods, such as whole grains, and too much unhealthy foods, including sweetened beverages, account for one in every five deaths globally.
“Poor diet is an equal opportunity killer,” said Dr. Ashkan Afshin, lead author on the study and an assistant professor at the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington. “We are what we eat and risks affect people across a range of demographics, including age, gender, and economic status.”
Afshin, who authored a global paper on obesity in 2017, emphasized that today’s study focuses on the effects of food on chronic health problems, such as heart disease and diabetes, independent of their connections to obesity. More than 130 scientists from nearly 40 countries contributed to the analysis, which was published today in the international medical journal . The paper is the most comprehensive analysis on the health effects of diet ever conducted.
Poor diets were responsible for 10.9 million deaths, or 22% of all deaths among adults in 2017, with cardiovascular disease (CVD) as the leading cause, followed by cancers and diabetes. They also resulted in 255 million disability-adjusted life years (DALYs), which equal the sum of years of life lost and years lived with disability. Poor diet represents 16% of all DALYs among adults globally.
In comparison, tobacco was associated with 8.0 million deaths, and high blood pressure was linked to 10.4 million deaths.
In 2017, CVD was the leading cause of diet-related deaths (9,497,300) and DALYs (207.2 million), followed by cancers (913,100 deaths and 20.2 million DALYs), diabetes (338,700 deaths and 23.7 million DALYs), and kidney diseases (136,600 deaths and 3.4 million DALYs).
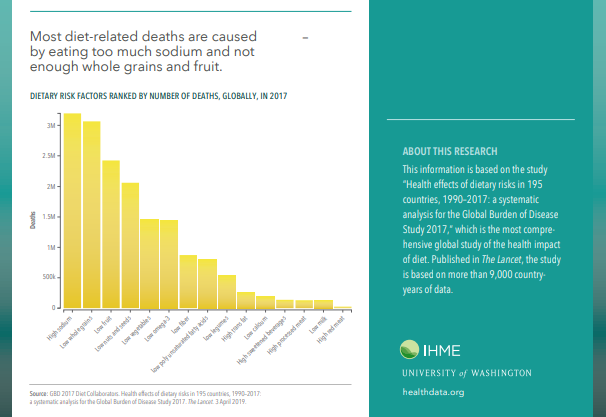
The study finds that while the impact of individual dietary factors varies across countries, three dietary factors — low intake of whole grains, as well as fruits, and high consumption of sodium — accounted for more than 50% of diet-related deaths and 66% of DALYs. The other 50% of death and 34% of DALYs were attributed to high consumption of red meat, processed meats, sugar-sweetened beverages, and trans fatty acids among other foods.
“
We are highlighting the importance of low consumption of healthy foods as compared to the greater consumption of unhealthy foods,” Afshin said. “Dietary policies focusing on promoting healthy eating can have a more beneficial effect than policies advocating against unhealthy foods.”
The largest gaps between current and optimal diets were observed for nuts and seeds, milk, and whole grains. Some of those gaps, Afshin said, result from food producers and manufacturers.
“
There is an urgent and compelling need for changes in the various sectors of the food production cycle, such as growing, processing, packaging, and marketing,” Afshin said. “Our research finds the need for a comprehensive food system intervention to promote the production, distribution, and consumption of healthy foods across nations.”
Harvard Professor Dr. Walter Willett, a co-author of the study, noted that the findings are consistent with a recent summary of randomized trials documenting benefits on risk factors for cardiovascular disease by replacing red meat with plant sources of protein.
“
Thus, adoption of diets emphasizing soy foods, beans and other healthy plant sources of protein will have important benefits for both human and planetary health,” he said.
While sodium, sugar, and fat have been the focus of diet policy debate in recent years, the assessment shows the leading risk factors resulting in death are diets high in sodium, low in whole grains, low in fruit, low in nuts and seeds, and low in vegetables. Each of these accounts for more than 2% of all deaths globally.
Among the world’s 20 most populous countries, Egypt had the highest rate of diet-related deaths (552 per 100,000) and DALYs (11,837 per 100,000) in 2017; Japan had the lowest rate of diet-related deaths (97 per 100,000) and DALYs (2,300 per 100,000).
Media contacts: About the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation
The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) is an independent global health research organization at the University of Washington that provides rigorous and comparable measurement of the world’s most important health problems and evaluates the strategies used to address them. IHME is committed to transparency and makes this information widely available so that policymakers have the evidence they need to make informed decisions on allocating resources to improve population health.
About the Global Burden of Disease study
The Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study is the largest and most comprehensive effort to quantify health loss across places and over time. It draws on the work of more than 3,600 collaborators from 146 countries and territories. The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation coordinates the study. The GBD 2017 study was published in November 2018 and includes more than 38 billion estimates of 359 diseases and injuries and 84 risk factors in 195 countries and territories.
Originally published at https://www.healthdata.org on March 26, 2019.
Infographic