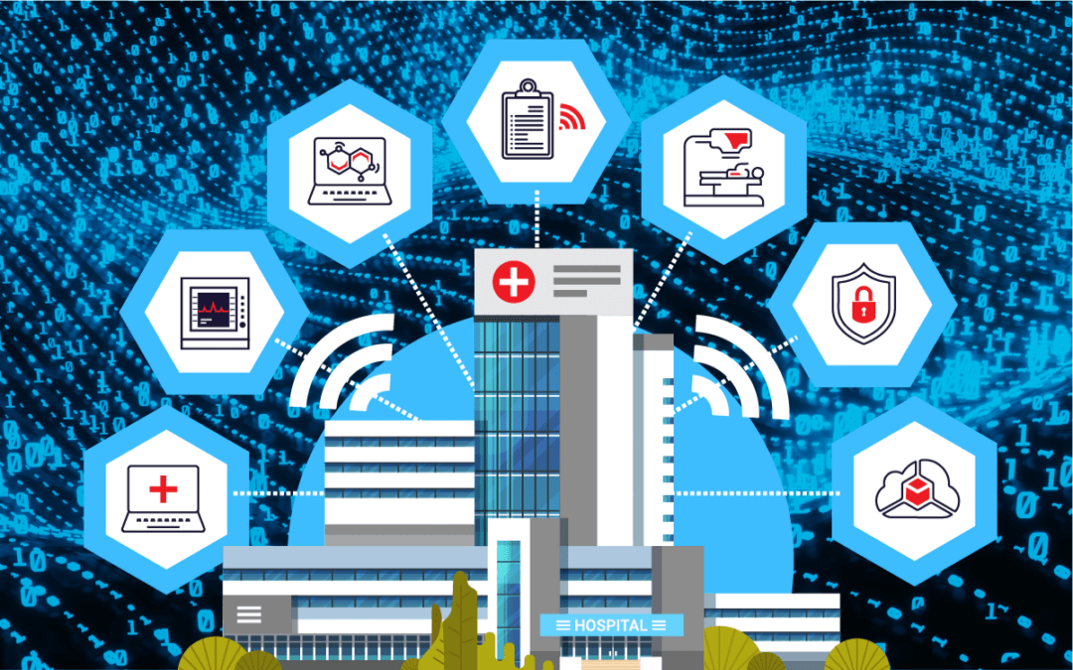
Smart hospitals leverage the power of technology to provide better patient experience, maximize operational efficiency and reduce costs.
By Michael Megarit
October 3, 2021.
Most people want a smooth hospital experience.
Unfortunately, most traditional hospital experiences are anything but: from jam-packed waiting rooms to overcrowded hospital rooms, overworked staff and the odd medical error, patients have little to look forward to.
Fortunately, things are beginning to change.
Around the world, hospitals are leveraging the power of Artificial Intelligence (AI), Big Data and the Internet of Things (IoT) to revolutionize the healthcare experience.
It is beyond doubt that tomorrow’s hospital will be smarter and more efficient.
These new age hospitals use innovative technology to deliver high quality care, improve patient experience and rationalize costs.
Their infrastructure makes extensive use of Artificial Intelligence (AI), Big Data and the Internet of Things (IoT) to create an integrated, efficient ecosystem that improves the patient experience, maximizes operational efficiency and reduces costs.
These new age hospitals use innovative technology to deliver high quality care, improve patient experience and rationalize costs.
These new technology-centric hospitals are dubbed “smart hospitals”.
While these novel hospitals are still a relatively new concept, they are already a massive success.
Indeed, the smart-hospital technology market is expected to achieve $77 billion at a 21.5% CAGR from 2018–2025.
Table of Contents (TOC)
- 1 — Smart Hospitals Improve the Quality of Care
- 2 — Smart Hospitals Improve Patient Experience
- 3 — Smart Technology Reduces Costs
- The Catch: Smart Hospitals Are Expensive To Build

1 — Smart Hospitals Improve the Quality of Care
With great innovation comes great promise.
Will these smart hospitals succeed in revolutionizing the traditional hospital model? How will they actually improve care? Is the smart hospital model universally applicable?
Here are 3 reasons why smart hospitals have the potential to change the healthcare paradigm forever — and one reason why they might not.
In 2016, John Hopkins published a study revealing that medical errors are the third leading cause of death in the US, responsible for more than 250K deaths per year.
In most cases, communication problems and inadequate information flows are to blame.
Thankfully, a host of revolutionary technologies are being integrated into hospitals to reduce these inefficiencies.
medical errors are the third leading cause of death in the US, responsible for more than 250K deaths per year.
In most cases, communication problems and inadequate information flows are to blame.
Smart hospitals are using cutting edge technologies such as hospital navigation, intelligent imaging platforms, medical robots, remote patient monitoring tools, medication management applications, communication tools, and EHRs to address the limitations of traditional providers.
Smart hospitals are using cutting edge technologies such as hospital navigation, intelligent imaging platforms, medical robots, remote patient monitoring tools, medication management applications, communication tools, and EHRs to address the limitations of traditional providers.
In fact, a recent report published by consultancy firm Frost & Sullivan found that smart hospitals are delivering higher standards of care than traditional hospitals:
- Smart patient tracking systems manage patient flow, treatment progress and discharge.
- Proper training and implementation of Electronic Health Records (EHRs) improve the hospital’s ability to provide excellent care and address health disparities.
- The use of AI rationalizes supply chain management, since algorithms process the large volumes of hospital data.
This helps doctors identify trends, diagnose conditions and improves efficiency and care quality. - Local healthcare teams are empowered due to data analysis obtained from different hospital departments.
smart hospitals are delivering higher standards of care than traditional hospitals, based on some tools such as: (1) Smart patient tracking systems; (2) Proper training and implementation of Electronic Health Records (EHRs); (3) The use of AI rationalizes ; (4) data analysis obtained from different hospital departments, etc
Furthermore, the Medical Internet of Things (MIoT), which refers to medical products that connect to the Internet and to each other, are also contributing to the revolution.
Furthermore, the Medical Internet of Things (MIoT) …are also contributing to the revolution.
Now, doctors can use a myriad of smart devices that collect and analyze data in real time:
- Wireless Vita Signs Monitors that measure blood oxygen levels, respiration rate, core body temperature, early warning score and blood volume levels without wires or invasive methods for the patients.
These devices connect to smartphones, computers, tablets and laptops and deliver real-time vital signs. - Digital Smart Connected Stethoscopes enable doctors to visualize and record sounds, share them with colleagues and upload them directly to the EMR.
- Smart Injection Devices allow doctors and patients to monitor injection administration.
- Smart ventilators and other interconnected devices that collect and share data.
How can collecting seemingly unrelated data help doctors improve the quality of care?
By leveraging the power of Machine Learning, a subset of AI.
Machine Learning’s powerful algorithms can analyze large pools of disparate data, detect patterns among millions of known diseases and provide useful recommendations that enable doctors to make the correct decisions in a timely manner.
This software saves precious time and analyzes data in a systematic and in-depth way that humans can’t.
Plus, machines work 24/7 and are never tired, which allows for constant data collection, analysis and treatment.
Ultimately, smart hospitals are increasing operational efficiency and reducing human errors.
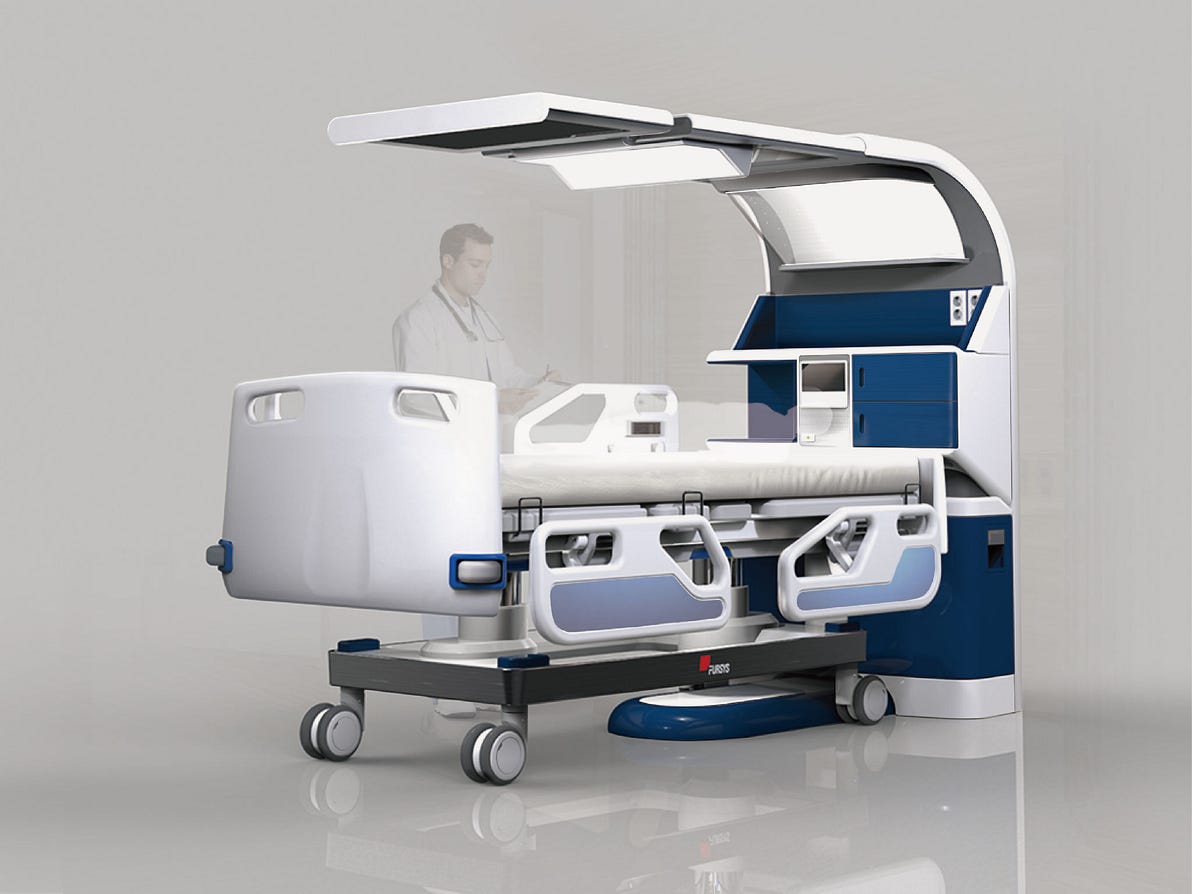
2 — Smart Hospitals Improve Patient Experience
A smart hospital is designed to be sensitive and responsive to the needs of patients, visitors and caregivers.
For example, the hospital rooms are equipped with “ smart beds “ that can communicate with the patient’s EHR, the care team and even the patient itself.
Thanks to a host of sensors and communication technology, the bed becomes an extra member of the care team:
- Sensors to help prevent falls and send alerts if the bed is in an unsafe position.
- Integrates with the nurse’s real-time locating system badges (RTLS), which are programmed to silence alarms when they enter a patient’s room.
- Personalized comfort settings: adjust the firmness of the bed, control entertainment, nurse call button provides audio confirmation of calls.
- Delivers verbal prompts that communicate to patients and caregivers.
- Monitors dozens of data points, such as bed position, patient weight and cardiopulmonary resuscitation mode.
- Electronically updates the patient’s medical record, including the number of times they turned or left their bed.
In addition, thanks to telehealth, doctors are now able to communicate, provide services and monitor patients remotely.
Whether in their hospital room or in the comfort of their own home, patients can access their doctor and receive medical attention anytime.
The advantages of telehealth are numerous: reduced costs, proactive treatments, less risk of infection, and convenient healthcare service.
Further, wearable technology enables doctors to monitor their patients in real time, as they walk around the hospital rooms and corridors.
Patients can also take the wearables home and transmit important health data directly to the hospital.
This live data transmission enables immediate analysis, early detection of problems and ultimately avoids unnecessary hospitalizations.
Also, AI technology gives doctors the ability to refill prescriptions electronically and even send them directly to the patient’s neighborhood pharmacy.
3 — Smart Technology Reduces Costs
Finally, traditional hospitals are under tremendous financial pressure.
Smart hospitals that leverage the use of technology can reduce operational costs in a variety of ways. In fact, McKinsey believes that implementing smart technology will help hospitals realize cost savings of more than 10% annually.
Here’s how.
First, smart technology reduces unnecessary hospital room expenses.
Thanks to remote patient monitoring, patients can consult their doctors and specialists from the comfort of their own home, eliminating travel costs and hospital room expenses.
Second, smart scheduling applications help hospitals implement efficient staffing policies.
By scheduling staff according to real patient flows, the number of open beds, emergency room capacity and equipment status, hospitals can reduce costly overtime pay and the need to hire temporary staff.
Third, smart technology helps to streamline time-consuming claims processing.
This technology automates the claims process, enabling providers to improve payment efficiency which results in significant savings in both staffing and repayment turnaround times.
Fourth, energy-saving technology can help hospitals save millions a year.
Toronto’s Humber River Hospital, recognized as North America’s first digital hospital by the Intelligent Health Association, is 41.8% more energy efficient that traditional hospitals.
As a result, they save $3.2 million a year in energy costs that they systematically invest back into patient care.
Clearly, smart hospitals are a revolutionary concept.However, there is one major obstacle to their widespread adoption: the cost.
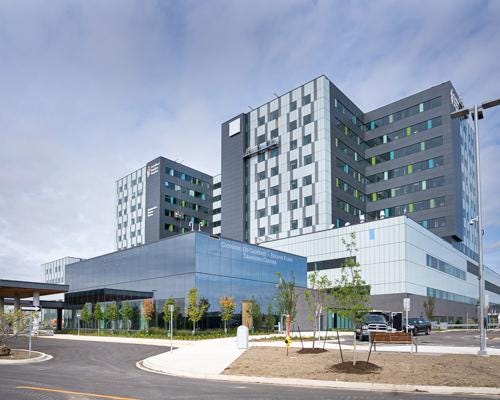

The Catch: Smart Hospitals Are Expensive To Build
Building a traditional hospital can cost anywhere from $52-$210 million. On average, the cost of building a 300,000 sq. ft. hospital with 120 beds stands at $112.5 million.
These averages do not include the cost implementing the sophisticated technology that a smart hospital requires. Installing this infrastructure and monitoring its smooth functioning can add millions to the bill.
In Canada, Mackenzie Vaughan Hospital, one of the nation’s first smart hospital which boasts 1800 full-time employees, 100 specialist doctors and 700 volunteers, cost a whopping $1.6 billion to build.
Building a traditional hospital can cost anywhere from $52-$210 million. On average, the cost of building a 300,000 sq. ft. hospital with 120 beds stands at $112.5 million.
In Canada, Mackenzie Vaughan Hospital, one of the nation’s first smart hospital which boasts 1800 full-time employees, 100 specialist doctors and 700 volunteers, cost a whopping $1.6 billion to build.
Michael Megarit is a partner with Cebron Group.
With over 25 years of domestic and international corporate finance experience,
he provides M&A and capital advisory to high-growth technology companies.
Unfortunately, not every city or country has the resources to finance such ambitious projects.
Thus, smart hospitals will remain the privilege of a wealthy few until the cost of technology decreases and becomes more accessible.
About the Author
Michael Megarit is a partner with Cebron Group.
With over 25 years of domestic and international corporate finance experience,
he provides M&A and capital advisory to high-growth technology companies.
Originally published at https://michaelmegarit.com on October 3, 2021.