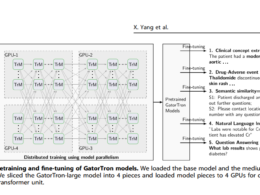
health
transformation
knowledge portal
Joaquim Cardoso MSc
Founder and Chief Researcher, Editor & Strategist
March 18, 2024
What is the message?
The landscape of AI prompt engineering is evolving rapidly, with recent research indicating that allowing AI models to autonomously optimize prompts may outperform human-engineered prompts.
This shift challenges the conventional role of prompt engineers and prompts the emergence of new job titles like LLMOps engineers.
Despite this evolution, prompt engineering, albeit in a different form, remains crucial in adapting generative AI for commercial applications.

This summary is based on the article “AI Prompt Engineering Is Dead > Long live AI prompt engineering”, published by IEEE Spectrum and written by Dina Jenkina on March 6, 2024.
What are the key points?
Proliferation of Prompt Engineering: Since the advent of ChatGPT in 2022, prompt engineering has become ubiquitous, with individuals and businesses leveraging it to optimize AI model performance for various tasks, from language processing to image generation.
Challenges and Inconsistencies: Despite widespread adoption, prompt engineering faces challenges such as inconsistency in performance across different models and datasets. Even sophisticated prompting strategies like chain-of-thought yield unpredictable outcomes.
Autotuned Prompts: Recent research suggests that allowing AI models to autonomously generate and optimize prompts can yield superior results compared to human-engineered prompts. Tools like NeuroPrompts demonstrate the effectiveness of this approach in enhancing image generation quality.
Evolution of Job Roles: As prompt engineering evolves, traditional job titles may give way to new roles like LLMOps engineers, who are responsible for the entire lifecycle of deploying AI products, including prompt optimization.
What are the key statistics?
Austin Henley notes that every business is exploring the use of AI for various use cases.
Rick Battle and Teja Gollapudi’s research found a lack of consistency in the impact of different prompt-engineering strategies on LLM performance.
The process of autonomously generating optimal prompts was found to be significantly faster, taking only a couple of hours compared to several days of manual searching.
What are the key examples?
Rick Battle and Teja Gollapudi’s study revealed that AI-generated prompts, including quirky references like Star Trek, often outperformed manually optimized prompts.
Intel labs’ NeuroPrompts tool showcased how autonomously generated prompts improved image generation quality compared to human-engineered prompts.
Conclusion
Prompt engineering is undergoing a paradigm shift, with AI models increasingly taking on the role of prompt optimization.
While this challenges traditional notions of prompt engineering, the evolution of job roles like LLMOps engineers indicates the continued importance of adapting generative AI for commercial applications.
Despite the uncertainties and rapid changes in the field, prompt engineering remains a vital component in harnessing the full potential of AI technologies.
To read the original publication, click here.