the health strategist
institute for strategic health transformation
& digital technology
Joaquim Cardoso MSc.
Chief Research and Strategy Officer (CRSO),
Chief Editor and Senior Advisor
October 19, 2023
One page summary
What is the message?
Public-private partnerships are instrumental in addressing global health inequities, and a successful example of such collaboration is the initiative between the United Nations Institute for Training and Research (UNITAR) and Takeda, a global biopharmaceutical company.
This partnership aims to improve patient access to critical plasma-derived therapies, emphasizing the importance of uniting diverse stakeholders, focusing on local solutions, and embracing the concept of shared value to create more resilient and equitable healthcare systems.

Key Takeaways
Unite Diverse Stakeholders:
Public-private partnerships bring together a diverse range of stakeholders, including governments, patient organizations, academia, healthcare professionals, and the private sector. This diversity of perspectives, knowledge, and resources is crucial in developing practical and impactful solutions to global health equity challenges.
Focus on Local Solutions:
Global health challenges have broad impacts, but the most effective solutions are often identified locally. The UNITAR-Takeda initiative empowers partner countries to design tailored solutions that strengthen their healthcare systems and improve local access to plasma-derived therapies. For example, efforts in Malaysia and Argentina are addressing plasma supply challenges at the local level.
Embrace Shared Value:
Public-private partnerships can drive sustainable solutions by aligning business interests with societal needs. This concept of shared value goes beyond corporate social responsibility and creates a framework for achieving progress toward health equity. The plasma initiative demonstrates how societal and business goals can intersect, benefitting patients and contributing to United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals.
Broaden the Partnership:
UNITAR is actively seeking more funding partners to join the initiative, encouraging a broader discussion on the potential of public-private partnerships to address global health challenges effectively.
Statistics
- The partnership between UNITAR and Takeda aims to address the global challenge of sustainable plasma supply.
- Plasma-derived therapies are essential for treating various rare and complex conditions, such as bleeding disorders, primary immunodeficiencies, and neuroimmunology diseases.
- Global patient demand for plasma therapies exceeds the available supply, leading to health inequities, particularly in low- and middle-income countries.
- The initiative contributes significantly to four of the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals: (3) good health and well-being, (4) quality education, (10) reduced inequalities, and (17) partnerships for the goals.
Examples
- In Malaysia, UNITAR is assisting local stakeholders, including policy-makers, patient groups, and physicians, to publish a paper addressing the country’s plasma supply challenges.
- In Argentina, a survey is being conducted to identify challenges faced by the country’s blood and plasma collection centers.
- The UNITAR-Takeda initiative illustrates how shared value can be realized through collaborations with long-term commitments, aligning business interests with societal needs for the benefit of patients and society as a whole.
- UNITAR is actively seeking additional funding partners to join the initiative, emphasizing the importance of diverse support from both private companies and public organizations to effectively address global health challenges.
Conclusion
The UNITAR-Takeda partnership serves as a powerful example of how public-private partnerships can drive transformative solutions to global health challenges, with the potential to inspire other organizations to explore novel approaches and address the urgent needs of patients worldwide.
DEEP DIVE

A vital new plasma initiative shows how public-private partnerships boost global health
World Economic Forum
October 16, 2023
We face an urgent need for transformative solutions to ensure that everyone, regardless of location or circumstances, has access to equitable healthcare. The COVID-19 pandemic has revealed health inequities that exist among and within countries, and it is clear that traditional methods of addressing healthcare system challenges in terms of delivery and access are no longer adequate today. Public-private partnerships offer great potential to reshape the global healthcare landscape and improve patient outcomes.
This type of partnership is embodied by the ongoing collaboration between the United Nations Institute for Training and Research (UNITAR) and Takeda, a global biopharmaceutical company. Last year, we announced a joint initiative to strengthen the resilience of health systems to meet patients’ need for plasma and plasma-derived therapies. This initiative focuses on developing local solutions to the global challenge of sustainable plasma supply leading to continuity of care, showcasing how shared goals can lead to transformative outcomes.
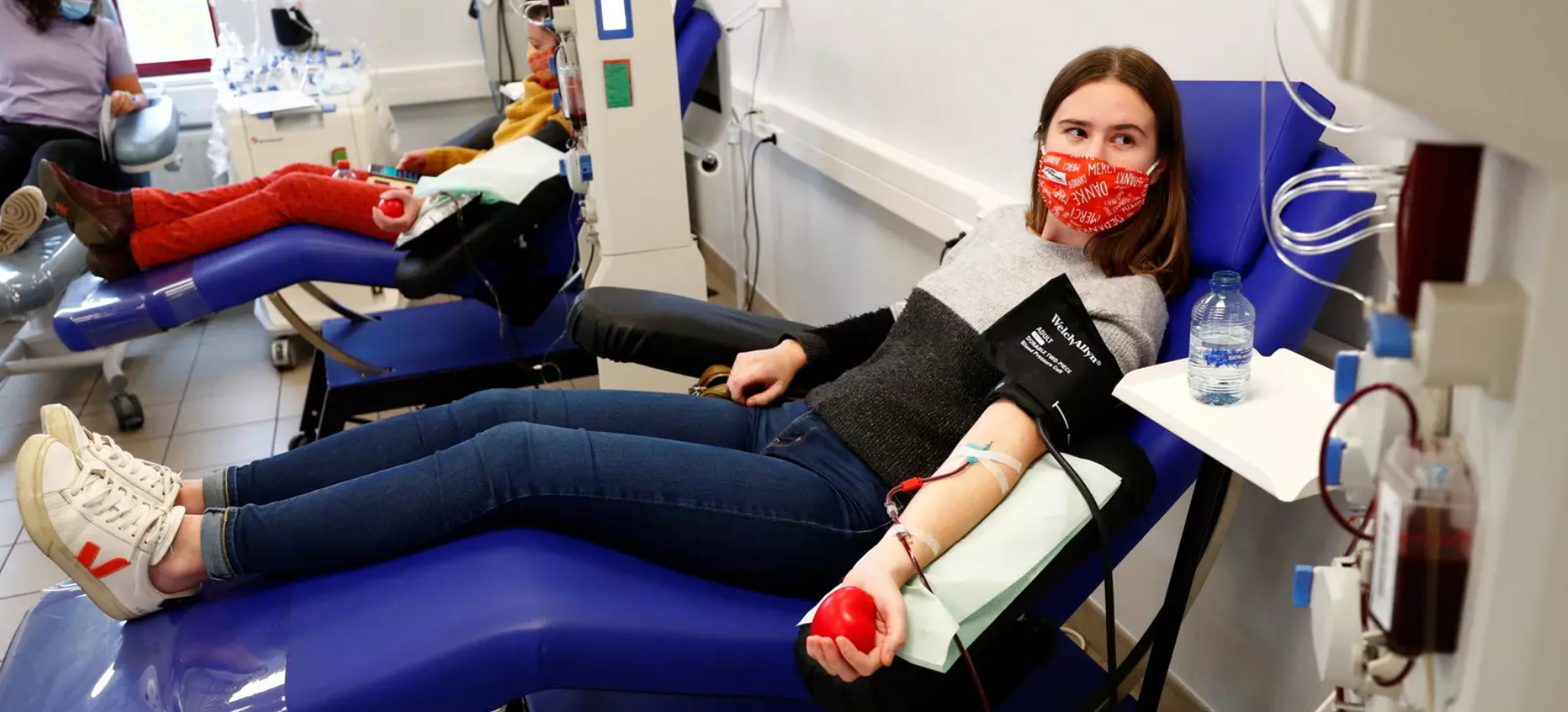
Plasma-derived therapies are critical, life-transforming treatments that can only be produced from human plasma and are used to treat a range of rare and complex conditions like bleeding disorders, primary immunodeficiencies and neuroimmunology diseases, among others. However, global patient need far outpaces available supply. This is largely due to increasing and earlier diagnosis and an inadequate supply of donated plasma due to policies and regulations that lag behind scientific progress. Furthermore, unequal access to vital plasma therapies, especially in low- and middle-income countries, leaves some patients with inadequate treatment and aggravates global health inequity.
The UNITAR-Takeda partnership highlights how public-private partnerships can create more resilient and equitable healthcare systems in three key ways:
- Uniting diverse stakeholders
- Focusing on local, tailored solutions to global challenges
- Embracing the concept of shared value
1. Uniting diverse stakeholders contributes to impactful outcomes
A striking feature of public-private partnerships in global health is the diversity of stakeholders they bring to the table with varying views. Developing practical and impactful solutions around global health equity challenges requires multi-area expertise, resourcing and skill sets from a range of stakeholders and organizations working collaboratively toward a common goal.
The plasma initiative forges connections between governments, patient organizations, academia, healthcare professionals and the private sector within working groups in partner countries. Each stakeholder contributes unique perspectives, knowledge and resources that inform the overall efforts to tackle challenges of plasma supply and patient access in their countries.
To support improved education on the global challenge, UNITAR launched an online knowledge hub, Plasma4Life, for the benefit of these working groups, policy-makers and the general public. Plasma4Life is intended to facilitate access to the latest scientific knowledge, public health data and best practices on plasma and plasma-derived therapies by leveraging the diversity and expertise of knowledge partners.
2. Focusing on local, tailored solutions supports tackling global challenges
While global health challenges, by definition, have wide-ranging impact around the world, practical solutions are best identified locally to create positive, sustainable solutions for patients. By zeroing in on neglected policy areas, the UNITAR-Takeda initiative empowers partner countries to design tailored solutions that strengthen their healthcare systems and improve local access to plasma and plasma-derived therapies.
In Malaysia, for example, UNITAR is currently supporting local working group members, including policy-makers, patient groups and physicians, to publish a paper about the country’s plasma supply challenges and opportunities. In Argentina, a survey to identify challenges faced by country’s blood and plasma collection centres is being conducted. Such collaborative local efforts can help drive improvements to the global plasma ecosystem with the goal of identifying and easing pressures on an already strained plasma supply.
3. Embracing the concept of shared value aligns societal and business goals
Public-private partnerships can drive sustainable solutions through shared value, a concept that describes the relationship between the private sector and society, identifying areas where societal and economic goals intersect and lead to positive and collective impact. Shared value goes beyond corporate social responsibility by aligning fair business interests with societal needs.
The plasma initiative illustrates how shared value can be realized through innovative collaborations with long-term commitments. Common goals of enabling a sustainable supply of plasma and achieving equitable patient access to plasma-derived therapies align societal and healthcare needs with business imperatives. This creates a sustainable framework to achieve progress toward health equity, benefiting patients now and in the future. Furthermore, this collaborative effort contributes significantly to the achievement of four of the United Nation’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): (3) good health and well-being, (4) quality education, (10) reduced inequalities, and (17) partnerships for the goals.
In this way, our initiative serves as a powerful reminder that the pursuit of global health equity is not only the domain of governments or international organizations. It is a collective endeavour in which the private sector can play a vital role as a knowledge partner, leveraging its resources and expertise to create positive and sustainable change.
Broadening the (public-private) partnership
While our partnership is committed to the long-term continuation of the initiative to improve lives of patients who could benefit from plasma-derived therapies, we also recognize that these types of alliances are most effective when industry is not represented by a single company or weighted to a particular bias. This is why UNITAR is now seeking more funding partners to join, including private companies and public organizations.
The tangible impact of public-private partnerships in advancing global health equity is undeniable. UNITAR, for example, is involved in several public-private partnerships in different global health areas, especially global surgery, value-based healthcare and breastfeeding. Takeda and UNITAR will continue to share learnings from our collaboration to encourage a broader discussion on the potential of public-private partnerships to develop transformative solutions to global health challenges. We hope that our work can serve as a roadmap and inspiration for other organizations to explore novel approaches that address urgent needs of patients around the world.
Originally published at https://www.weforum.org