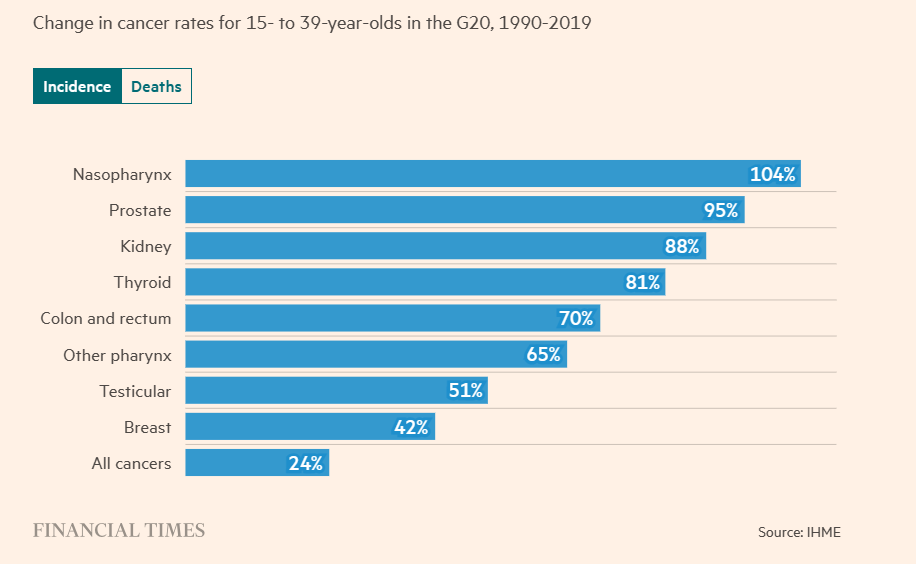health strategy portal
multidisciplinary institute for
health strategy and digital health
Joaquim Cardoso MSc
Chief Research and Strategy Officer (CRSO),
Editor in Chief and Senior Advisor
June 18, 2023
Key Message(s):
In conclusion, the rise in cancer cases among millennials presents a pressing concern.
- The estimated global cost of cancer from 2020 to 2050 is projected to be $25.2 trillion, impacting economic growth due to the loss of working-age individuals.
- Further research is required to fully understand the causes and risk factors associated with early onset cancer.
- Increased awareness, early detection, and targeted interventions are essential to mitigate the impact of this growing trend.
This is an Executive Summary of the article “The unexplained rise of cancer among millennials”, published on the Financial Times, authored by “Sarah Neville and Amy Borrett”
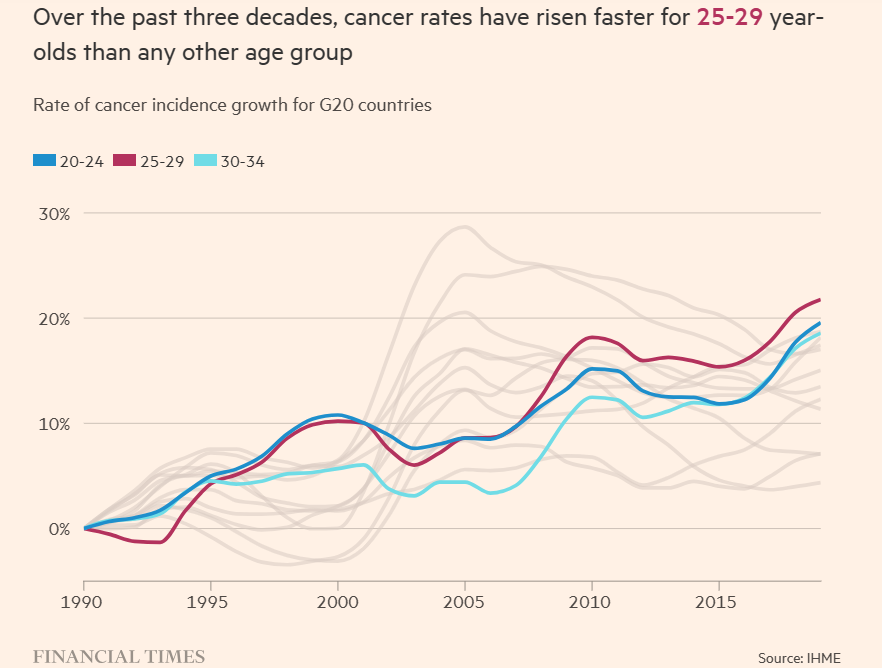
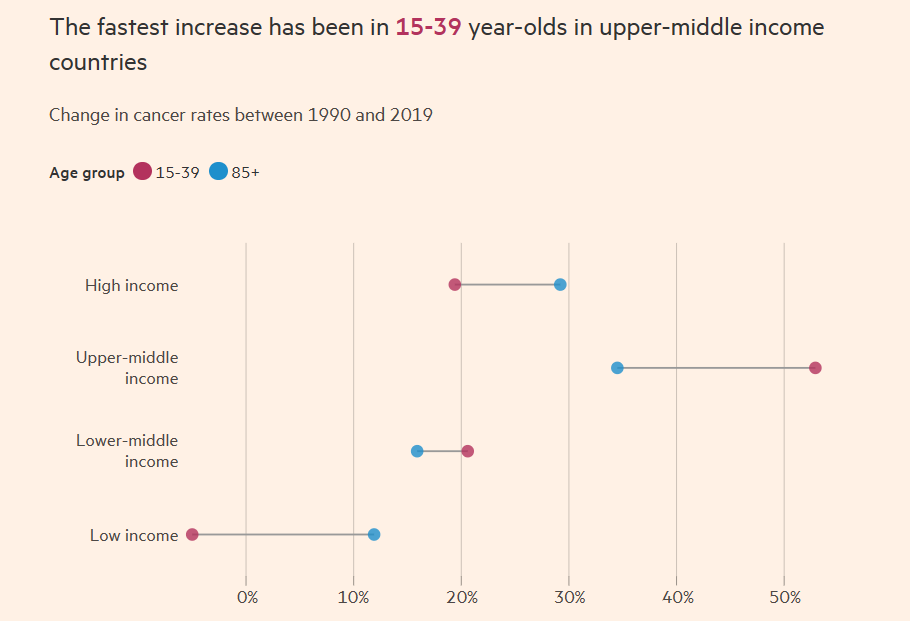
Over the past three decades, cancer rates have risen faster for millenials (25–29y) than any other age group —Why is that?
The incidence of cancer among millennials, individuals under the age of 50, has witnessed a significant and unexplained increase over the past three decades.
This rise has led epidemiologists to consider it an epidemic.
Cancer rates in the G20 countries have risen by 22% among 25- to 29-year-olds between 1990 and 2019, with rates for 20- to 34-year-olds reaching their highest level in 30 years.
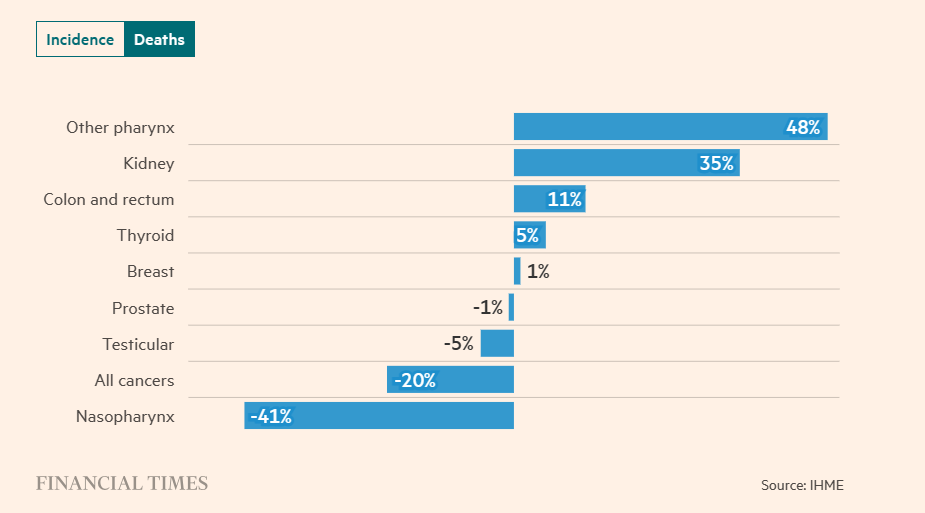
Meanwhile, cases among older age groups have declined.
Researchers have yet to identify a definitive explanation for this trend, but they are exploring various factors.
One possible clue lies in the types of cancer affecting young people, such as colorectal cancer, which has increased by 70% among 15- to 39-year-olds in G20 nations.
One possible clue lies in the types of cancer affecting young people, such as colorectal cancer, which has increased by 70% among 15- to 39-year-olds in G20 nations.
While age remains the biggest predictor of cancer risk, changes in nutrition, lifestyle, and the microbiome, the collection of microbes in the gut, are being considered as potential contributing factors.
While age remains the biggest predictor of cancer risk, changes in nutrition, lifestyle, and the microbiome, the collection of microbes in the gut, are being considered as potential contributing factors.
The microbiome is thought to play a crucial role in overall health, including digestion, immune system regulation, and protection against disease-causing bacteria.
Changes in diet, specifically the consumption of food high in saturated fat and sugar, have been linked to alterations in the microbiome that can negatively impact health.
Researchers suggest that the rise in early onset cancer may be connected to changes in the microbiome caused by modernized diets and lifestyle changes starting in the mid-20th century.
Furthermore, the increase in gastrointestinal cancers among younger individuals supports the potential link with diet.
Antibiotic use, medications, sedentary lifestyles, changes in sleep patterns, and exposure to bright light at night are among the other changes occurring in parallel, making it difficult to pinpoint a single cause.
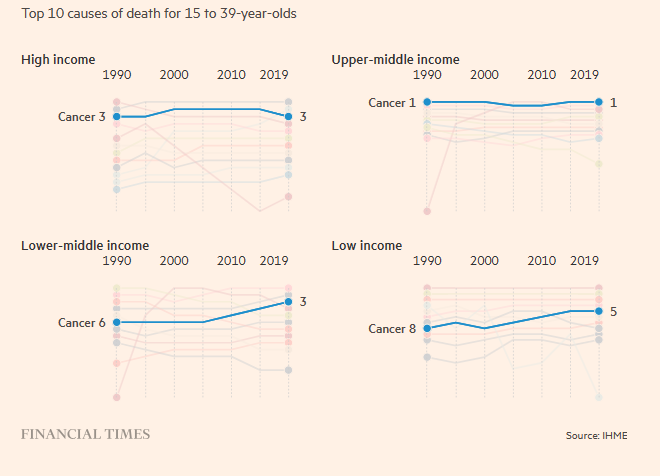
The rise in early onset cancer has significant economic, clinical, and social implications.
Survivors face a higher risk of long-term conditions and secondary cancers, posing future healthcare burdens.
The estimated global cost of cancer from 2020 to 2050 is projected to be $25.2 trillion, impacting economic growth due to the loss of working-age individuals.
The estimated global cost of cancer from 2020 to 2050 is projected to be $25.2 trillion, impacting economic growth due to the loss of working-age individuals.
Consequently, there is a growing demand for earlier cancer screening programs to detect cancer in younger populations.
Recognizing the differences in clinical features and molecular structures of early onset cancers, researchers suggest the need for tailored treatments.
However, delayed diagnoses and lack of awareness among younger individuals about cancer symptoms contribute to the problem.
It is crucial for healthcare professionals to remain vigilant and consider cancer as a possibility in younger patients.
Selected Image(s)