medRxiv preprint
Gert Johannes Kruger Marais, Nei-yuan Hsiao, Arash Iranzadeh, Deelan Doolabh, Annabel Enoch, Chun Yat Chu, Carolyn Williamson, Adrian Brink, Diana Ruth Hardie
posted December 24, 2021.
uq.edu.au
This article is a preprint and has not been certified by peer review.
It reports new medical research that has yet to be evaluated and so should not be used to guide clinical practice.
Infographic
Abstract
The Omicron variant is characterised by more than 50 distinct mutations, the majority of which are located in the spike protein.
The implications of these mutations for disease transmission, tissue tropism and diagnostic testing are still to be determined.
We evaluated the relative performance of saliva and mid-turbinate swabs as RT-PCR samples for the Delta and Omicron variants.
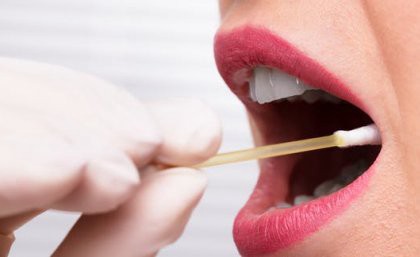
- The positive percent agreement (PPA) of saliva swabs and mid-turbinate swabs to a composite standard was 71% (95% CI: 53–84%) and 100% (95% CI: 89–100%), respectively, for the Delta variant.
- However, for the Omicron variant saliva and mid-turbinate swabs had a 100% (95% CI: 90–100%) and 86% (95% CI: 71–94%) PPA, respectively.
This finding supports ex-vivo data of altered tissue tropism from other labs for the Omicron variant.
Reassessment of the diagnostic testing standard-of-care may be required as the Omicron variant becomes the dominant variant worldwide.
Competing Interest Statement
The authors have declared no competing interest.
Additional information
See the original publication
Originally published at https://www.medrxiv.org on December 24, 2021.
Mid Turbinated Nasal Swabs
https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/downloads/lab/NMT-Specimen-Collection-Infographic.pdf