This is a republication of the article “ Joinvasc: Organizing the Full Cycle of Stroke Care with Universal Coverage”, with the title above.
Health Institute — for continuous transformation
Joaquim Cardoso MSc
Founder and Chief Researcher, Editor and Advisor
December 14, 2022
ORIGINAL PUBLICATION

Joinvasc: Organizing the Full Cycle of Stroke Care with Universal Coverage
NEJM
Henrique Diegoli, MD, MSc, Pedro Magalhães, MD, MBA, Márcia Makdisse, MD, PhD, MBA, Carla Heloísa Cabral Moro, MD, Paulo França, PhD, and Alexandre Longo, MD
December 14, 2022
The stroke care delivery program developed over decades in Joinville, Brazil, incorporates an integrated practice unit, robust data collection and analysis, community partnerships with the public and private sector, and interdisciplinary care throughout the stroke care cycle, including primary care, acute prehospital care, acute in-hospital care, and postacute care.
Summary
Patients with stroke in developing countries frequently have unmet needs due to fragmented care delivery, lack of access to effective treatment, and an absence of outcome metrics.
Joinvasc is a program aimed at improving stroke outcomes throughout the entire care cycle for the population of Joinville, Brazil.
Joinvasc started with clinical data measurement in 1995 and currently includes a stroke unit with a multidisciplinary team, a stroke registry, a patient association, public health care managers, and researchers.
Joinvasc started with clinical data measurement in 1995 and currently includes a stroke unit with a multidisciplinary team, a stroke registry, a patient association, public health care managers, and researchers.
Data collection is population based with a 5-year follow-up, including quality metrics, patient-reported outcomes, costs, and societal economic burden.
These data reveal unmet patient needs and are used in learning cycles with the professionals and managers.
Over the past few decades, Joinvasc has developed multiple strategies to improve outcomes, such as stroke prevention programs and care pathway design encompassing prehospital, in-hospital, and posthospital care.
Over the past few decades, Joinvasc has developed multiple strategies to improve outcomes, such as stroke prevention programs and care pathway design encompassing prehospital, in-hospital, and posthospital care.
Best medical practices were adopted for the stroke unit, thrombolysis, and thrombectomy.
The program is funded by Brazil’s public health care system, Sistema Único de Saúde, with universal access to care.
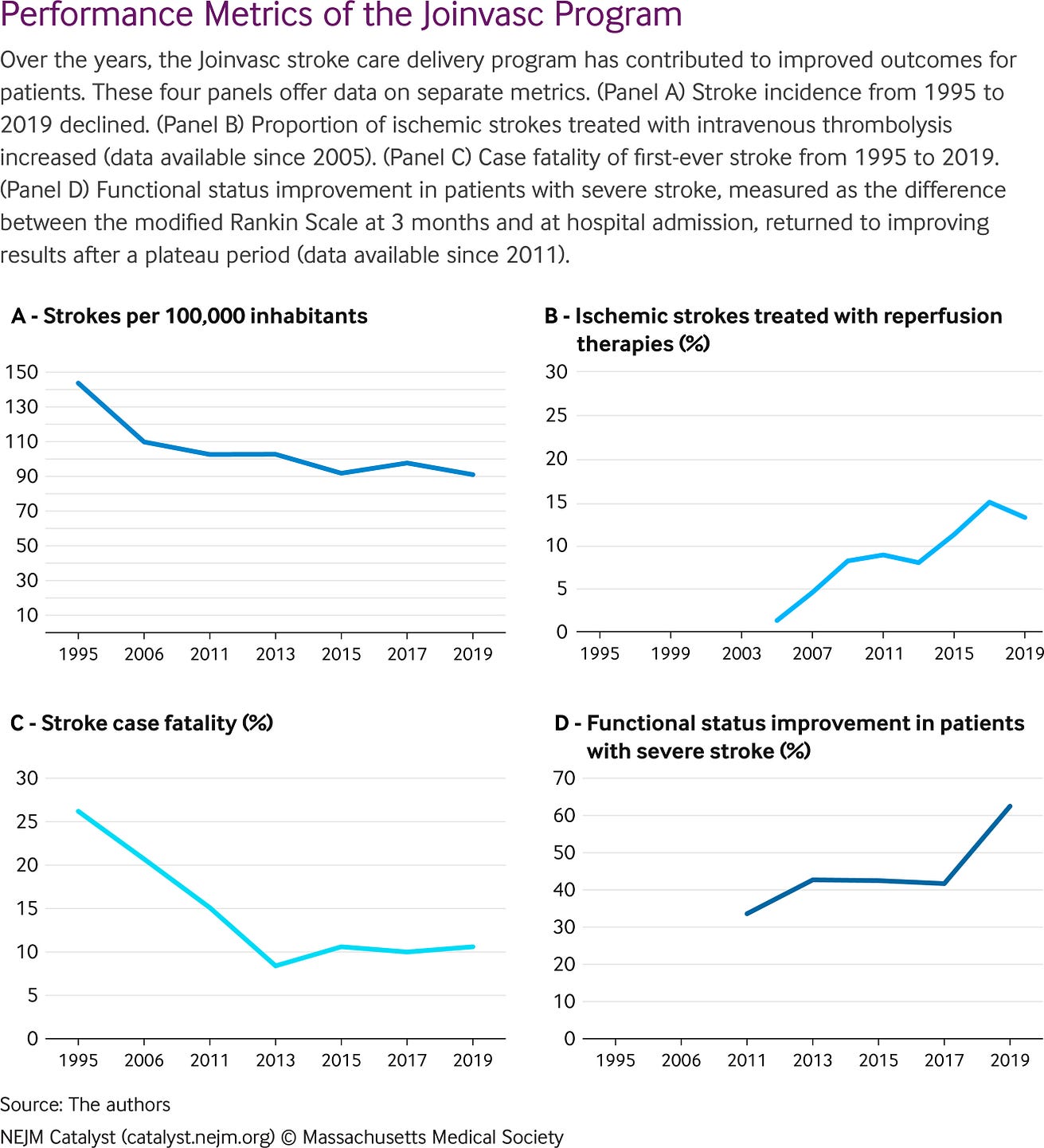
Achievements for the city’s population over 25 years include
- a 37% reduction in stroke incidence (to 91 per 100,000 in 2018–2019 from 143.7 per 100,000 in 1995),
- a 59% reduction in case fatality (to 10.6% in 2018–2019 from 26.2% in 1995), and an
- 86% increase in the proportion of patients with functional improvement after the stroke (to 62.5% in 2018–2019 from 33.6% in 2010–2011).
The Joinvasc case study demonstrates that value-based health care can be incorporated into settings with limited resources.
Changes were data driven, with improvement cycles led by a multidisciplinary team over decades of collaborative efforts.
Originally published at https://catalyst.nejm.org on December 14, 2022.












