Linkedin
Chartis
November 1, 2022
Chief Researcher and Editor:
Joaquim Cardoso MSc.
health transformation . portal
November 1, 2022
Telehealth Has Notable Staying Power, Hovering at Around a 10% Adoption Rate [vs. 1% pre-pandemic, US]
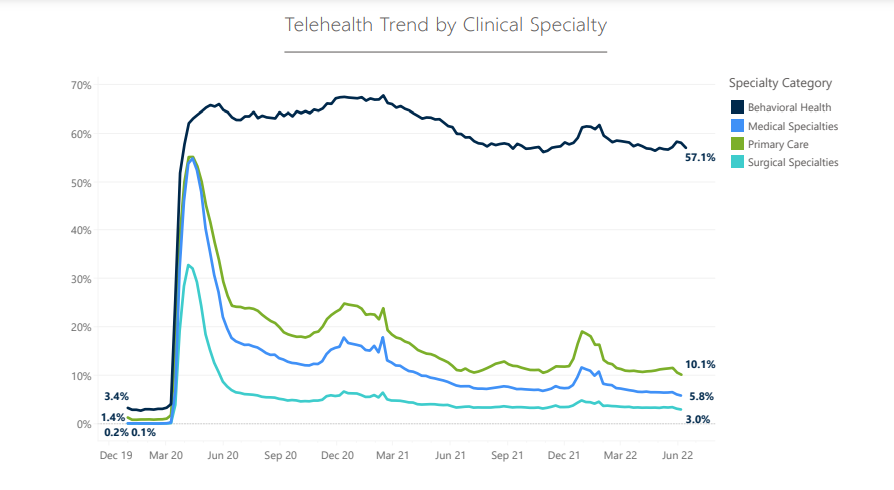
Telehealth Trend
Before the COVID-19 pandemic, patients received care at their doctor’s office.
In the last 2 years, this expectation-from patients, doctors, and insurers alike-has dramatically shifted.
Now, as we examine telehealth adoption across more than 2 full years with the pandemic as a backdrop, several factors are emerging that explain variation in adoption across the United States.
Namely, as COVID-19 shifts from pandemic to endemic, we’re now seeing that telehealth has established a prominent and lasting role in healthcare delivery across various geographies, patient demographics, and clinical service areas.
Namely, as COVID-19 shifts from pandemic to endemic, we’re now seeing that telehealth has established a prominent and lasting role in healthcare delivery across various geographies, patient demographics, and clinical service areas.
Why It Matters:
As healthcare organizations plan for the sustained use of telehealth, understanding adoption benchmarks and trends will better inform ongoing planning efforts related to telehealth’s long-lasting role in healthcare delivery.
In our updated trend analysis, we reviewed 5 key areas of telehealth adoption to identify where we see the greatest impact-and infer where it is likely to remain in the future.
We examined:
1.Overall Adoption.
- Two years into the pandemic, year-over-year trends show a downward trajectory of telehealth adoption.
- However, even as the national rate now hovers around 10%, this rate is much higher than the pre-pandemic levels of less than 1%.
- All indications point toward telehealth having notable staying power.
2.Demographic Adoption.
- While all age groups adopted telehealth at a similar rate during the early stages of the pandemic, a split is emerging, with those aged 18–44 having the highest steadying rate of adoption (15% of outpatient visits), and those aged 65 and older accounting for the lowest adoption rate (5% of outpatient visits).
- This signals that there is potentially a combination of stronger preference and clinical appropriateness for in-person care, and a less compelling telehealth experience among older patients.
3.Geographic Adoption.
- Certain regions across the U.S.-such as New England-are showing higher overall adoption of telehealth.
- This may foster greater regional agreements, reciprocal credentialing, licensure, and payment coverage.
- However, such regional variation may leave an ever-increasing gap for low-adopting states to catch up to the digitally forward care models being adopted elsewhere in the U.S.
4.Telehealth Modality Adoption.
- Telehealth programs should consider not just video visit offerings but also telephonic access options for patients, which have become quite common in several states across the country.
- Asynchronous use cases are still slow to catch on, comparatively, but are starting to catch on in some states to supplement real-time modalities like phone and video.
5.Clinical Adoption.
- Given the longitudinal trends of telehealth adoption over the last 2+ years, clarity is now gained on what a new normal is likely to be across clinical service lines.
- Behavioral health remains the clear highest adopter (57%), while primary care and medical specialties have established telehealth as permanent components of their care models.
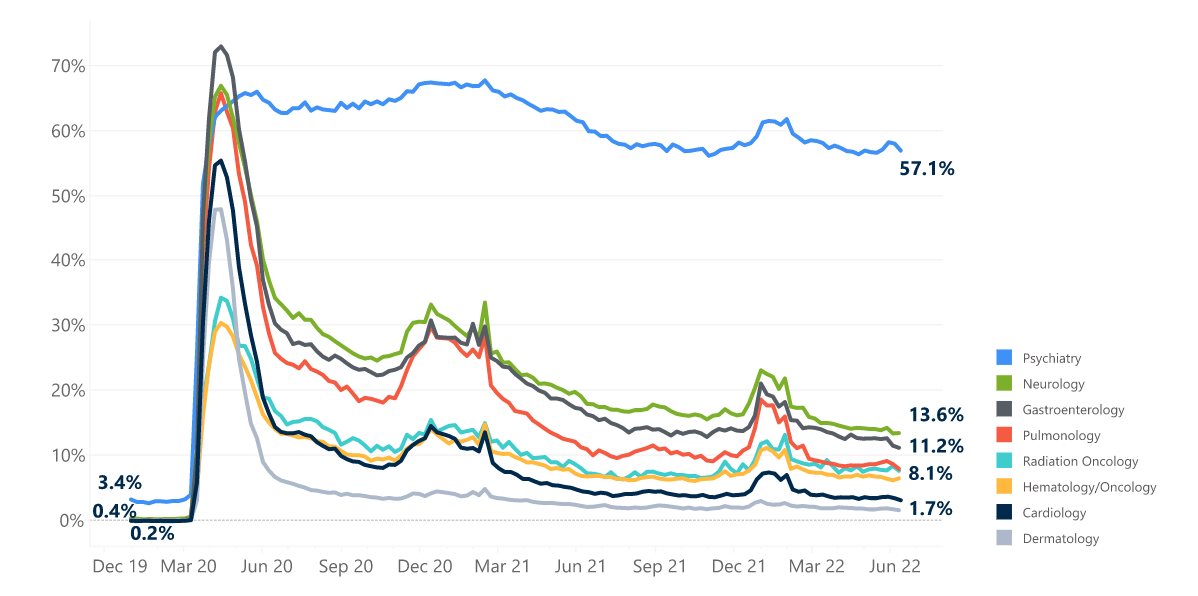
Telehealth Trend by Medical Specialty
What’s Next:
Adoption trends from 2021 to 2022 confirm that telehealth has become an established component of many clinical service lines and care models.
Over the coming years, expect these adoption rates to be baselines with greater experimentation of additional use cases to drive telehealth higher as more familiarity and innovation take hold to drive adoption higher.
As provider organizations continue to set their course forward with telehealth, several considerations will be important:
- Making virtual visits available to patients will remain important, even if utilization varies across service lines or patient cohorts.
- A successful patient retention strategy should include telehealth since most virtual visits are being conducted with patients who have existing relationships with their providers.
- Telehealth can be a viable solution in more clinical specialties and with broader patient groups than might be expected.
- Providers looking to integrate behavioral health services into traditional access points like primary care or Emergency Department care should strongly consider a digital-first model of care for patients presenting with such needs, given the widespread adoption of telehealth in behavioral health specialties.

Looking ahead, telehealth will continue to play an important role for health systems to maintain patient relationships and advance care models across service lines.
Taking into account a greater number of factors (like the unique demographics or technology utilization patterns of a state) will help provider organizations benchmark future telehealth adoption in their local context and design telehealth programs to best meet their patients’ needs.
Originally published at https://www.linkedin.com.